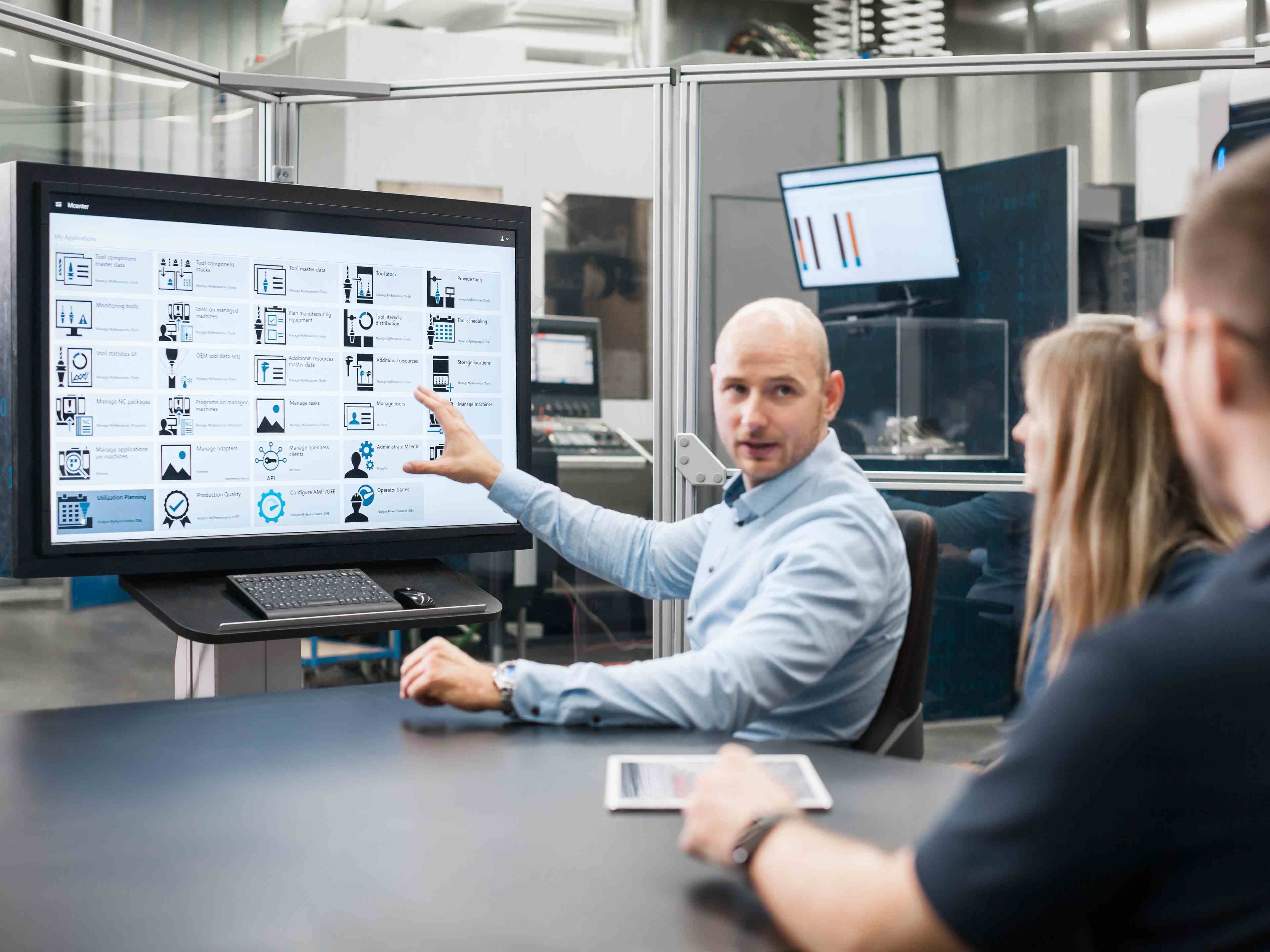
Main Functionalities
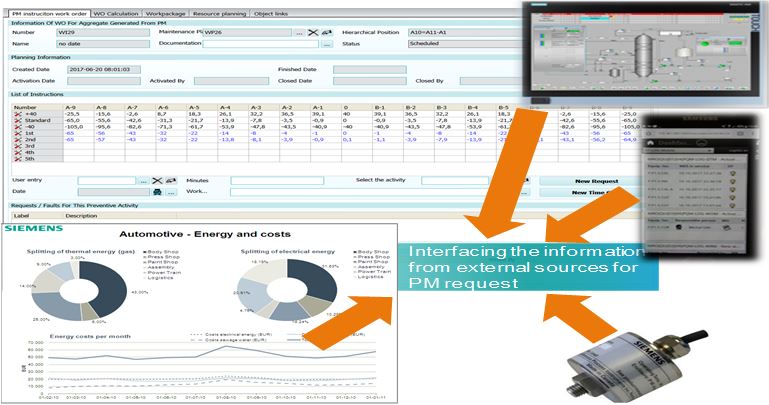
- SIMATIC IT Preactor APS is designed to be easily integrated with other business system to allow the simple retrieval of any required data, be that works order information from your ERP/MRP system or updates on operation progress from an MES. They can be tightly integrated with enterprise resource planning (ERP), accounting and forecasting software, spreadsheets, manufacturing execution system (MES) and shop floor data collection (MIS) systems, the companies are able to monitor the state of execution against plan
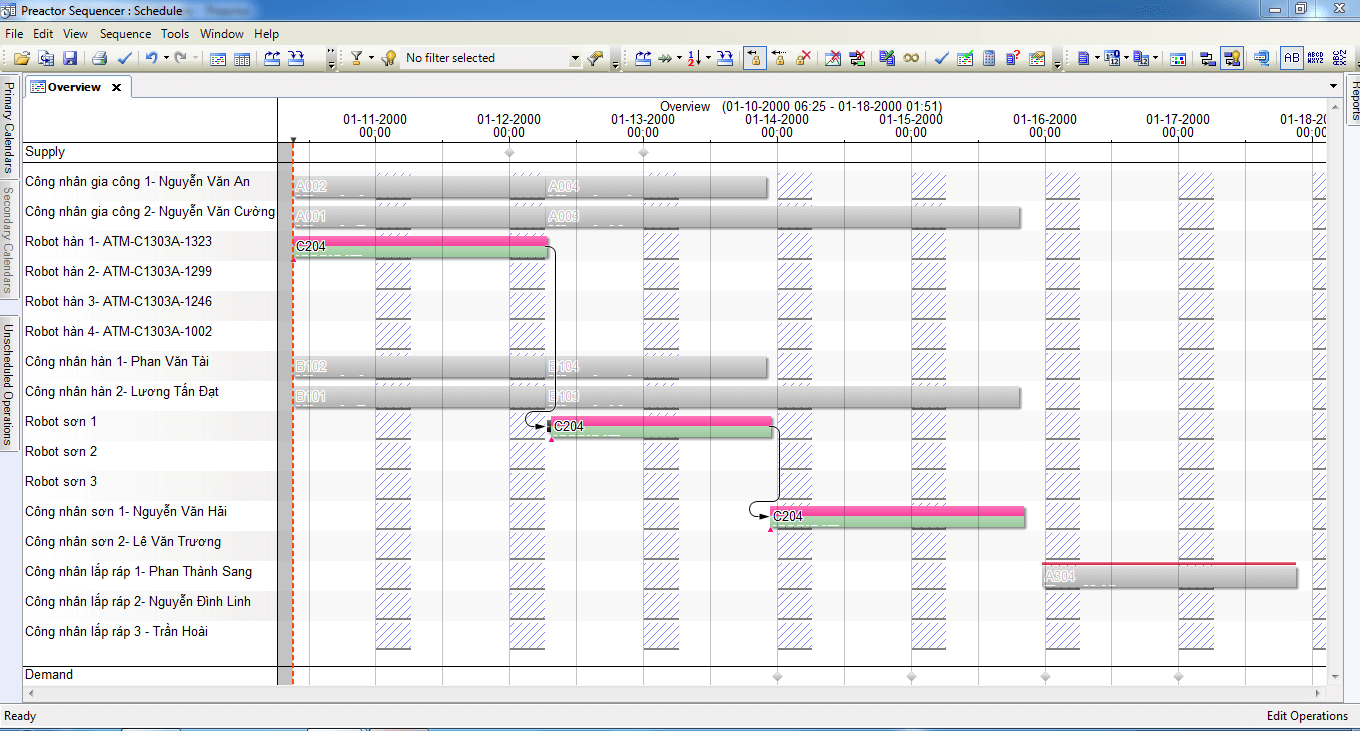
- It uses order based scheduling to which the user can apply a ranking or weighting in order to priorities the orders.
- It schedules based on availability of resources, additional constraints and the materials required for the order. During the scheduling process Preactor APS Standard can take in to account different operation run speeds on different resources, use sequence dependent changeover times based on operation attributes and allow overlaps and slack time between operations.
- The user is also able to implement customer specific rules about how materials are consumed and visualize their assembly process from raw materials through to finished goods and sales orders in the Material Explorer The user can see where shortages will occur and choose to keep them as a constraint or ignore them.
Key Benefits
SIMATIC IT Preactor Advanced Planning
- Decision support for long term strategy Production load balancing and smoothing
- Rapid master production schedule generation
- Ability to respond quickly to changes in demand
SIMATIC IT Preactor Advanced Scheduling
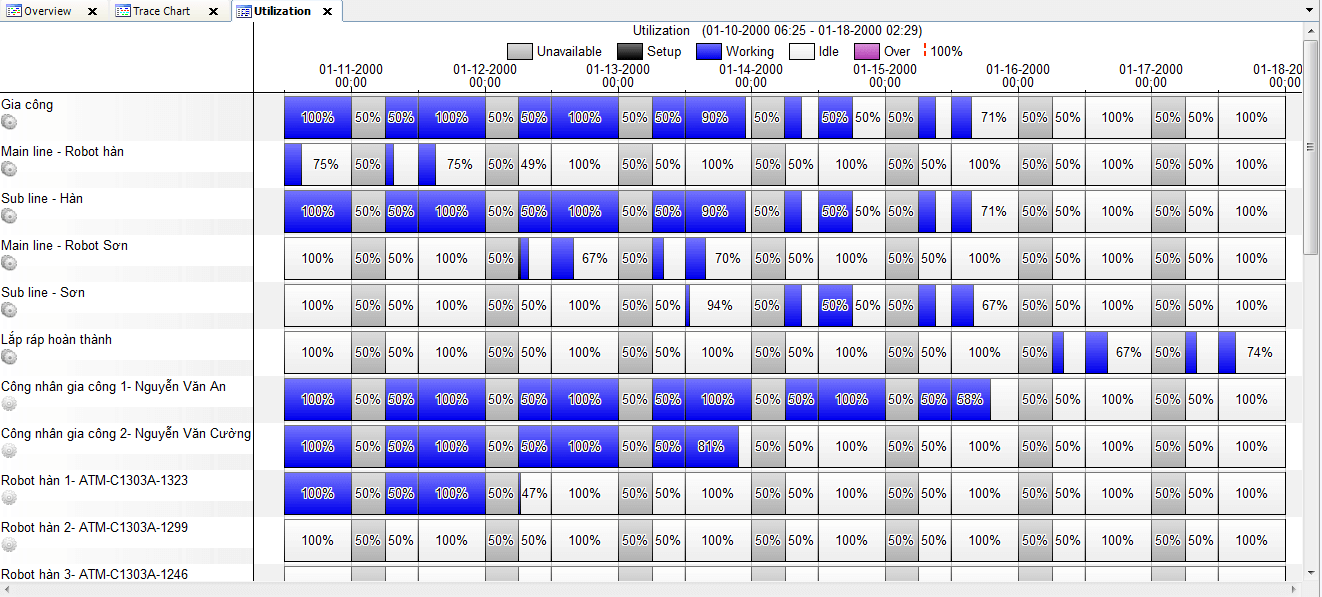
- Better resource utilization
- Reduction of setup and changeovers
- Reduction of inventory and WIP
- Detailed visibility of the production load
- Faster ‘what if’ scenario modelling
- Improved on-time delivery
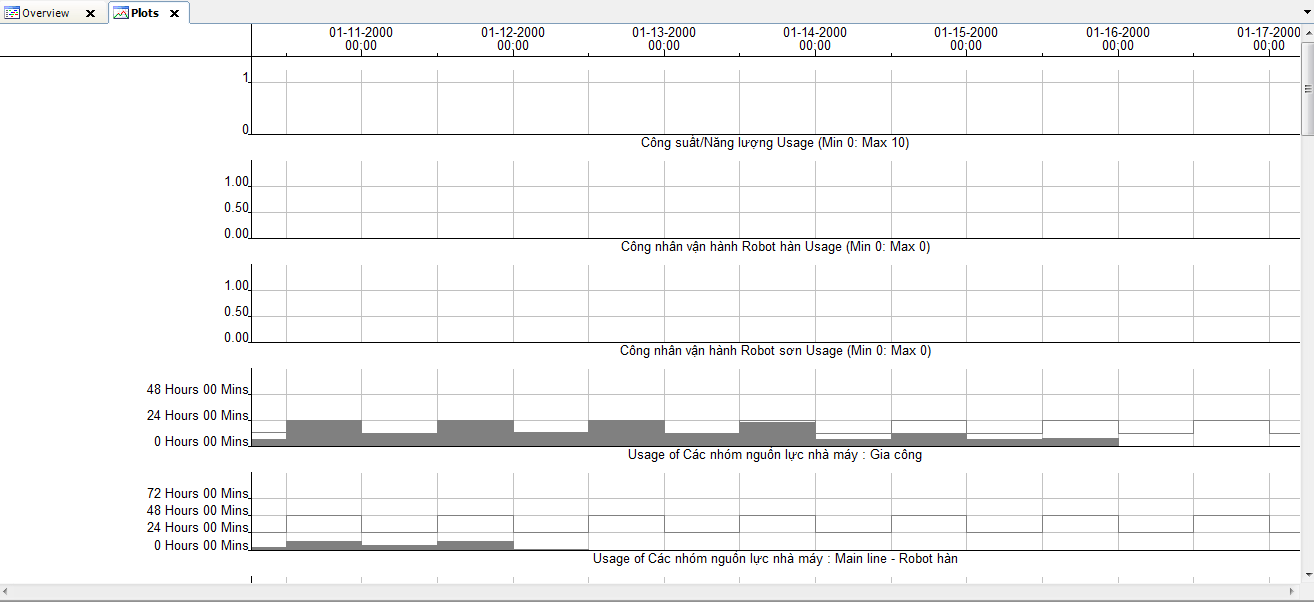
- Considers detailed production demand to provide production sequence, work to list;
- Predicts effects of change in production, interruptions, machine breakdown, scrap;
- Reacts to real time production efficiency;
- Load balance across multiple resources considering eg constraints, materials shelf life;
- Visualize the current load, see the impact of unexpected events, ask what-if questions and compare alternatives before the decision is made.
- Optimize production operations by reducing or eliminating nonvalue-added activities such as setup or waiting time. Highlighting potential problems allows action to be taken to balance demand and capacity.
- They are used by small and mid-size companies and large corporations to help meet demands made by their customers and beat the increasingly global competition.